Power battery connectors, also known as power battery interfaces, plugs, and sockets, generally refer to devices that connect two active components to transmit electric current. The role of power battery connectors is straightforward: they bridge the gap between interrupted or isolated circuits within the circuit, allowing electric current to flow and enabling the circuit to perform its intended function. The form and structure of power battery connectors vary greatly, with various types of connectors available depending on factors such as the SEDlication, power, and environment. The safe and reliable operation of power battery connectors is crucial to ensuring the normal operation of electric vehicle power systems. They are an indispensable part of the electric vehicle power system, with safety, reliability, and environmental friendliness being key considerations in their design.
Basic Components of Power Battery Connectors:
The basic structural components of power battery connectors include contact components, insulators, housings (depending on the variety), and accessories, with the contact components being the core parts that complete the electrical connection function. Generally, contact pairs consist of positive and negative contact components, which complete the electrical connection through the engagement of the positive and negative contact components. The positive contact component is a rigid part, typically cylindrical (pin), square (pin), or flat (sheet), and is usually made of brass or phosphor bronze.
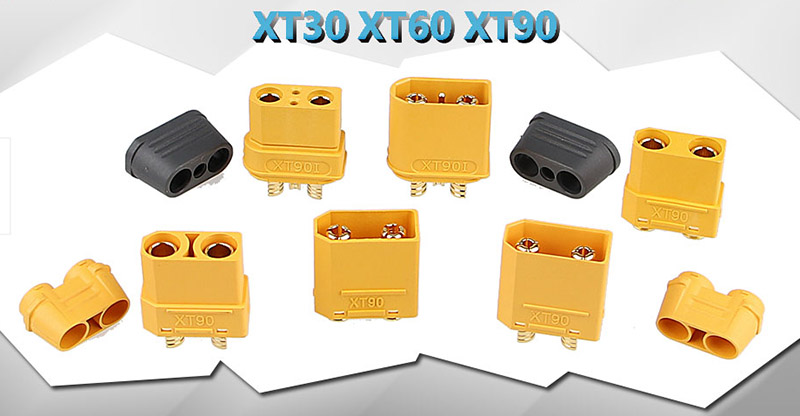

Amass
XT30 XT60 XT90 power connector diagram
The negative contact component is the key part of the contact pair, relying on its elastic structure to undergo elastic deformation when engaged with the pin, generating elastic force to form a tight contact with the positive contact component, completing the connection. There are many types of structures for negative contact components, including cylindrical (with slots or reduced diameter), fork-shaped, cantilever beam-shaped (longitudinal grooves), folded (longitudinal grooves, 9-shaped), box-shaped (square holes), and hyperbolic wire spring holes.
The reliability of the contacts in power battery connectors is related to the contact resistance between the contact pairs. Generally, lower contact resistance is preferred to reduce functional losses caused by contact resistance. It also reduces contact heating; excessively high contact heating can increase the contact resistance value. Additionally, excessive heat, if poorly dissipated, can soften the metal, accelerate surface oxidation and wear, deteriorate connector quality, and even cause connector housing softening, deformation, and aging.
 Guangdong SED Co., Ltd.
Guangdong SED Co., Ltd.
 +86 13763213143
+86 13763213143
 info@dmictech.com
info@dmictech.com


